| Version 1 (modified by , 16 years ago) (diff) |
|---|
MutekH tutorial for SoCLib platform
This guide explain how to run MutekH on a SoCLib hardware simulator. This is allow easy experimentation with advanced multi-processor programming.
You are highly encouraged to first follow the MutekH as Unix process quick start guide which introduces more basic concepts.
MutekH for SoCLib can be compiled for Mips, Arm, PowerPC processors. Other processors are available with different platforms.
The SoCLib platform
The MutekH kernel source code is fully configurable and can be tweaked to adapt hardware platform and application needs. Configuration is handled by a dedicated tool which check dependencies and other relationships between the large set of available configuration tokens.
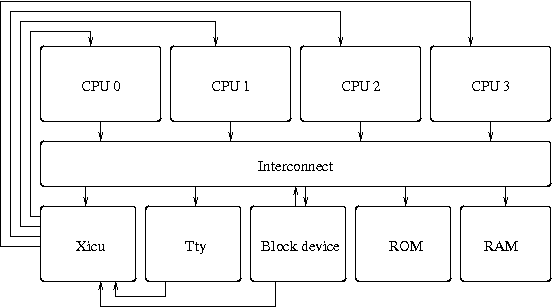
The example below explains how to setup a SoCLib hardware simulator with 4 RISC processor (Mips, Arm or PowerPC).
Getting SoCLib
We now need to have a working SoCLib install. SoCLib installation is explained here: https://www.soclib.fr/trac/dev/wiki/InstallationNotes
SoCLib platform description
The SoCLib source tree contains a platform dedicated to this tutorial:
soclib/soclib/platform/topcells/caba-vgmn-mutekh_soclib_tutorial/
Getting the cross-compilers
SoCLib installation nodes already provides a way to get cross-compiler, if you don't already have them, MutekH holds a tool to build a complete cross-compilation toolchain:
The script is in tools/crossgen.mk:
$ tools/crossgen.mk [prints some help] $ tools/crossgen.mk all TARGET=mipsel-unknown-elf
The MutekH part
Getting the sources
svn co -r 1183 https://www-asim.lip6.fr/svn/mutekh/trunk/mutekh
Writing the example source code
Note: This example is available directly from examples/hello directory in source tree.
- Writing the source code in
hello.c#include <pthread.h> pthread_mutex_t m; pthread_t a, b; void *f(void *param) { while (1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&m); printf("(%i) %s", cpu_id(), param); pthread_mutex_unlock(&m); pthread_yield(); } } int main() { pthread_mutex_init(&m, NULL); pthread_create(&a, NULL, f, "Hello "); pthread_create(&b, NULL, f, "World\n"); }
- Writing the
Makefileobjs = hello.o
Writing the MutekH configuration
The MutekH configuration for the 4 Mips processors platform is in the examples/hello/config file.
This file only holds information about the application (here a simple pthread application) and relies upon files in the examples/common directory for the platform definitions.
Have a look to the BuildSystem page for more information about configuration system and configuration file format.
The MutekH API reference manual describes all available configuration tokens.
Platform description
The MutekH software uses hardware enumeration to get details about available hardware in the platform, so the CONFIG_ARCH_DEVICE_TREE token is defined in the examples/common/platforms-soclib.conf configuration file. It will let the kernel get the platform layout description from a FlattenedDeviceTree which will be built into the kernel.
Therefore, the build also compiles the correct FlattenedDeviceTree from the platform name.
The current FlattenedDeviceTree source file is examples/common/pf_soclib_tutorial_ppc.dts, (for arm), (for mips).
Compiling the application along with MutekH
The MutekH kernel and the application may be built out of the source tree.
Change to the SoCLib platform directory and apply the following steps to experiment with out of tree compilation. You have to setup the following variables:
MUTEKH_DIR- Path to MutekH source tree
APP- Path to application source
CONFIG- MutekH configuration file name
BUILD- MutekH build option list (target architecture, cpu type, …)
See the config.mk file in the tutorial platform directory for more information.
$ cd soclib/soclib/platform/topcells/caba-vgmn-mutekh_soclib_tutorial $ make MUTEKH_DIR=/path/to/mutekh
This will build the MutekH kernel along with the application. You can still build MutekH separately as explained in the first part. The simulator can then be built using:
$ cd soclib/soclib/platform/topcells/caba-vgmn-mutekh_tutorial $ make system.x
Execution
You can optionally pass an alternative kernel to the simulator, but this defaults to the correct kernel name if you followed the tutorial until here.
$ ./system.x mutekh/kernel-soclib-ppc.out
You may want to refer to other articles and documents available from the main page to go further with MutekH.
The SoCLib home page provides a livecd image with more advanced examples ready to compile and run. These examples are using older MutekH revisions though.
Other more advanced topics and guides are available from the Main page.
Attachments (2)
-
arch.png (4.5 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
Architecture
- output.png (72.6 KB) - added by 16 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip

